
The central nervous system (CNS) is one of the most complex and vital parts of the human body. It consists primarily of the brain and spinal cord, working together to control movement, thought, sensation, and emotion. Acting as the body’s command center, it receives information from sensory organs, processes that information, and sends out responses that guide every aspect of life.
However, when this intricate network becomes damaged, the results can be devastating. Disorders of the central nervous system can affect motor function, memory, mood, and even basic bodily functions such as breathing and heart rate. Fortunately, medical science has made remarkable progress in understanding and treating CNS disorders — especially through the development of regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy.
Understanding Central Nervous System Disorders
CNS disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that disrupt the normal function of the brain or spinal cord. These disorders may arise from genetic factors, trauma, infections, vascular problems, immune dysfunction, or degenerative changes associated with aging. Some of the most common and impactful conditions include:
1. Parkinson’s Disease
A progressive neurological disorder that affects movement, Parkinson’s results from the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in a region of the brain called the substantia nigra. Symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
MS is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath, the protective covering of nerve fibers. This leads to communication problems between the brain and body, causing muscle weakness, fatigue, and impaired coordination.
3. Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia, marked by memory loss, confusion, and cognitive decline. It results from the buildup of abnormal protein deposits (amyloid plaques and tau tangles) that disrupt neural communication and destroy brain tissue.
4. Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, depriving brain cells of oxygen and nutrients. Depending on the area affected, a stroke can lead to paralysis, speech problems, or severe cognitive impairment.
5. Spinal Cord Injury
Physical trauma to the spinal cord can result in permanent changes in strength, sensation, and body function below the site of the injury. Recovery is limited because the CNS has a reduced capacity for self-repair.
The Challenge of CNS Regeneration
Unlike other tissues in the body, the brain and spinal cord have a limited ability to regenerate after injury. Once neurons die, they generally cannot be replaced. This has made CNS repair one of the most challenging areas in medicine.
For decades, treatment for CNS disorders focused primarily on symptom management — using medications, rehabilitation, and supportive care to improve quality of life. However, these approaches rarely addressed the underlying cause of neuronal loss. The need for therapies that could actually repair or replace damaged neural tissue led to the rise of regenerative medicine.
What Is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a rapidly advancing field that aims to restore, replace, or regenerate damaged cells, tissues, and organs. It uses cutting-edge biological techniques such as stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and gene therapy to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
Stem cells — often called the body’s “master cells” — have the unique ability to develop into various types of cells, including neurons and glial cells found in the CNS. This characteristic makes them an invaluable resource for treating conditions that were once thought to be irreversible.
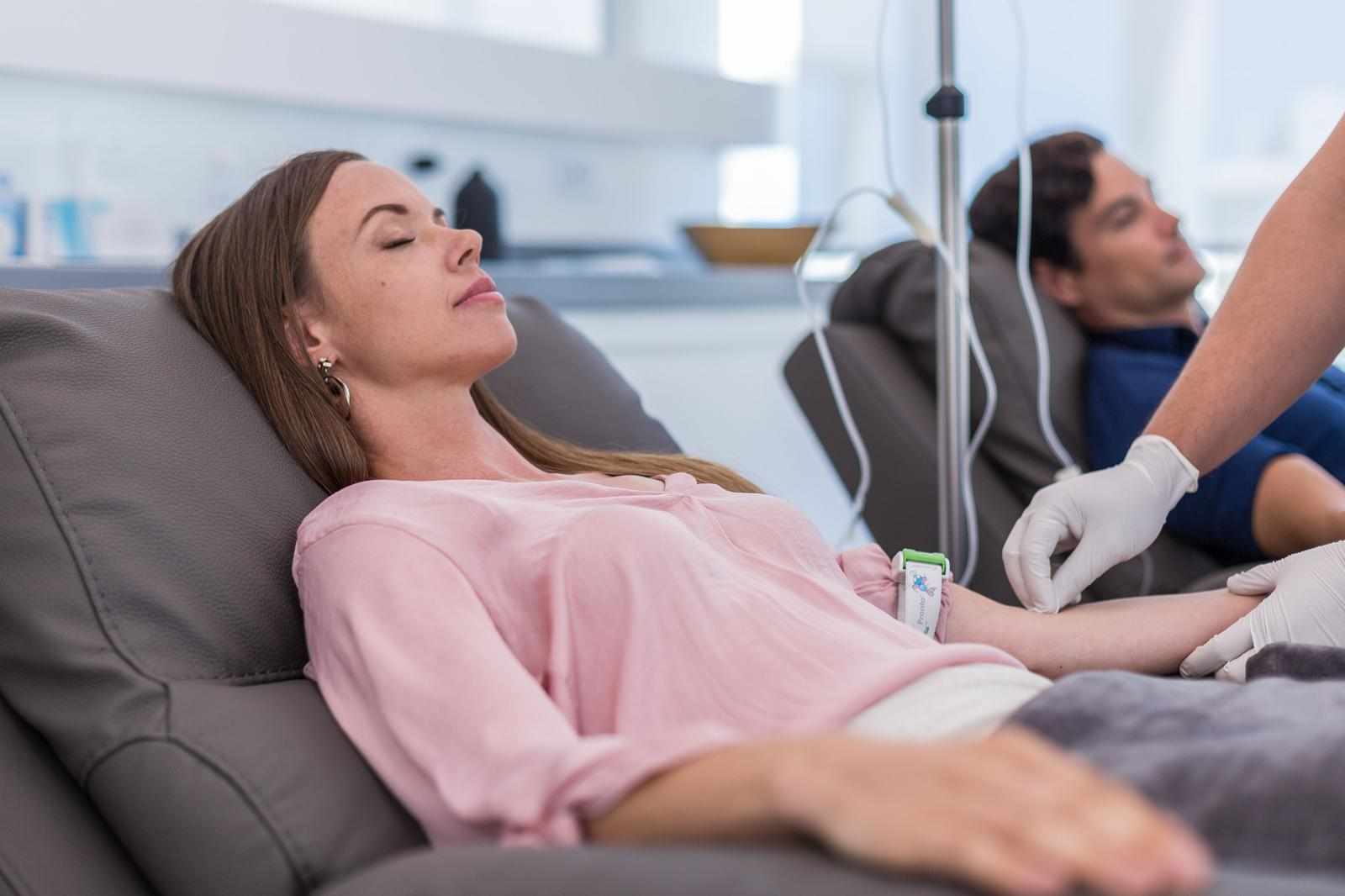
Stem Cell Therapy and the Central Nervous System
Stem cell therapy has become one of the most promising approaches for repairing CNS damage. Through precise medical application, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from sources such as bone marrow or umbilical cord tissue can be introduced into the body to support healing and regeneration.
Here’s how stem cell therapy may help in CNS disorders:
Neural Regeneration: Stem cells can differentiate into neurons or support existing neurons, potentially restoring lost neural connections.
Reduction of Inflammation: Many CNS disorders involve chronic inflammation that accelerates nerve damage. MSCs release bioactive molecules that help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Protection Against Cell Death: Stem cells secrete neurotrophic factors — substances that support neuron survival and growth — protecting the brain and spinal cord from further degeneration.
Improved Function: Clinical studies have shown encouraging results in improving motor function, memory, and overall neurological performance in patients receiving stem cell-based therapies.
regenerative medicine is at the forefront of patient-centered innovation. Research and clinical applications of stem cell therapies aim to unlock the body’s own repair systems, offering a new horizon for individuals facing CNS challenges.
Modern Regenerative Therapies in Development
In addition to stem cell therapy, several next-generation regenerative treatments are under exploration to enhance CNS recovery:
Gene Editing: Technologies like CRISPR are being investigated to correct genetic mutations that cause neurodegenerative diseases.
Exosome Therapy: Exosomes, tiny particles released by stem cells, play a key role in cell communication and tissue repair. They are being tested for their ability to deliver healing signals to damaged neurons.
Neurotrophic Factor Delivery: Scientists are developing methods to deliver growth factors directly to injured brain or spinal cord tissue to encourage regeneration.
Tissue Engineering: Lab-grown neural tissue may one day replace or repair sections of the CNS that have been damaged by injury or disease.
The Future of Central Nervous System Regeneration
While many regenerative treatments are still being refined, the progress made in recent years is remarkable. The idea that brain and spinal cord damage could one day be reversed was once unimaginable — but today, it’s becoming an achievable goal.
Ongoing clinical trials around the world are evaluating the safety and effectiveness of these therapies, and early results are encouraging. For patients living with CNS disorders, regenerative medicine represents not only innovation but also hope — the hope for recovery, independence, and restored quality of life.
Conclusion
The central nervous system is the foundation of human function and identity, and its disorders can profoundly affect every aspect of life. Modern regenerative therapies, especially stem cell-based treatments, are transforming the way these conditions are understood and managed.
As research continues, regenerative medicine stands as a powerful bridge between science and healing — offering possibilities that were once beyond reach. For those seeking evidence-based care and advanced treatment options, trusted medical innovation sources like https://rehealth.com/ provide valuable insight into the future of CNS health and recovery.







Write a comment ...